How To Identify Critical Data for The Enterprise
08 February 2024


Ratan Verma
Practice Head - Data ManagementRatan Verma, Practice Head - Data Management brings a wealth of experience in Information Management and Data Privacy domains, advising CIOs/CDOs, and helping to set up...
What is Critical Data?
Critical Data is the data that is essential for making key decisions, meeting regulatory requirements, or delivering essential services.
It may often include master data and sensitive information like financial data, customer information, and intellectual property but can also encompass operational data critical for day-to-day functions.
Importance of Critical Data
- Helps prioritize data security and governance efforts.
- Ensures high-quality data for accurate decision-making.
- Reduces risks associated with data breaches and compliance failures.
- Can potentially save costs by focusing resources on the most important data.
Hence, critical data identification is a crucial aspect of data management that involves identifying and categorizing data elements that are essential to an organization's operations, decision-making processes, and overall success.
Factors to consider when working with critical data

Business Impact
Corporations need an understanding of critical data directly linked to the organization's core functions and objectives. Critical data based on this parameter involves understanding how each data element contributes to business processes, decision-making, and strategic goals.
Data Classification
This involves knowledge of data categories based on its importance and sensitivity. Critical data based on this parameter may include customer information, financial records, intellectual property, regulatory compliance data, and any other information crucial for business continuity.
Enterprise Risk
There are potential risks associated with the loss, corruption, or unauthorized access to critical data. For enterprise data practitioners, they must have a clear understanding of the impact of data breaches or data loss on the organization's reputation, compliance, and financial standing.
Regulatory Compliance
These are critical data elements that fall under regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements. Also included is data needed to ensure that the organization's handling of critical data aligns with industry-specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA).
Data Lifecycle Management
It is crucial to manage critical data throughout its lifecycle, from creation and processing to storage and disposal and applying appropriate security measures and access controls at each stage of the data lifecycle.
Stakeholder Involvement
Critical data management involves relevant stakeholders in the identification process, including business leaders, data owners, and IT professionals. Collaborating to determine the criticality of specific data elements to different business units.
Data Mapping
Creating data maps is a crucial step during critical data management. This process involves visual representation of the flow of critical data across the organization. Understanding how data moves through systems and processes helps in identifying potential vulnerabilities.
Data Quality
Critical data management must involve ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of critical data. Also, companies should implement data quality measures to maintain the integrity of essential information.
Data Encryption and Security
To ensure protection of critical data, applying encryption and robust security measures is a crucial step (especially during transmission and storage). Companies should implement access controls to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Critical data should be integrated into disaster recovery and business continuity plans to ensure that data can be recovered swiftly in the event of system failures, natural disasters, or other emergencies.
Documentation
There should be detailed documentation of the criteria used to identify critical data. Maintaining an inventory of critical data elements and their associated metadata is crucial for traceability and to adapt to evolving business processes.
Regular Review and Updates
Lastly, it is imperative to periodically review and update the list of critical data elements to adapt to evolving business needs and changes in data importance. By systematically identifying and managing critical data, organizations can enhance their ability to make informed decisions, protect sensitive information, and maintain business continuity in the face of potential risks and challenges.
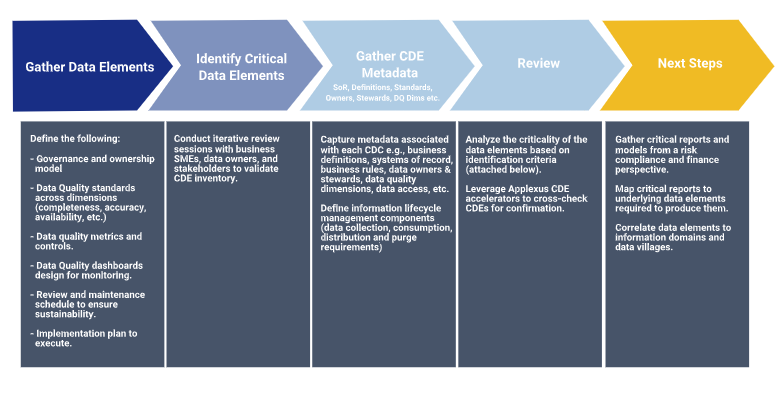
Approach to identify Enterprise Critical Data
Applexus proposes a multi-step approach for identification and development of Critical Data Elements (CDE) inventory from a risk, compliance, and finance perspective. This approach actively provides stakeholders to gather and analyze the requirements that provides business needs; and continuously adapt to changes in the business environment.
| Identification Criteria | Example |
|---|---|
| Is the data element directly or indirectly used in regulatory and external compliance reports? | SOX reports, FDA submissions, SEC reports |
| Is the data element directly or indirectly used in management, analytical, financial, risk & KPI related reports? | Year-end sales reporting, loan and portfolio level reports, balance sheet, income statement, quarterly reports |
| Does the data element help identify financial, business, and reputational risks and impact? | Mortgage loan performance reports, capital plan, fraud discovery, clinical trials reports, delinquency reports |
| Is the data element a critical input to risk models? | Probability default, fraud and delinquency risk models, credit rating calculation model |
| Does the data element impact business processes and is it used across multiple business lines? | Customer information, product master, master data |
| Is the data element used in calculating critical metrics and business rules? | Revenue calculations, employee retention reports |
| Is the data element part of key information category (a.k.a. Subject Area) or entity? | Marketing, human resources, supply chain operational data |
| Does the data element support data integrity and help identify uniqueness (match & search) across entities? | Account Number, SSN, Customer ID, Loan ID etc. |
| Is the data element time-sensitive or have high expectations across DQ dimensions? | Loan rates, account balances, credit rating, personal data, date of birth, SSN etc. |
| Does the data element have organizational ramifications if unavailable or incorrect? | Account balances, liabilities, date of birth, SSN etc. |
| Does the data element have multiple downstream dependencies? | Data marts, data lakes, data hubs, operational data stores |
| Does the data element alleviate overhead from a people, process, and technology perspective? | Supports automation, reconciliation, or prevents manual intervention |
In Conclusion
Robust management of critical data is the cornerstone of effective and efficient data management practice for an enterprise. Critical Data Management is the foundation for effective decision-making, risk management, compliance, and overall operational resilience in the modern data-driven business landscape.
Furthermore, identifying critical data allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently. By focusing on protecting and managing the most essential data assets, organizations can optimize their investments in data security, storage, and management. Lastly, mishandling or compromise of critical data can significantly damage an organization's reputation. Identifying and protecting sensitive information helps maintain trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders.









